Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction
Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Mechanism of a Reaction, Elementary Reactions, Inhibitor & Activation Energy Curve for an Endothermic Reaction etc.
Important Questions on Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction
For a hypothetical reaction , the activation energy for forward and backward reactions are and respectively. The heat of reaction is
The potential energy diagram for four reactions are given below
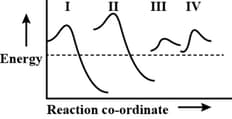
Which one of the following statements about these diagrams is incorrect?
The factors which influence the rate of reaction are :
Concentration: Greater the concentrations of the reactants, faster is the rate of reaction.
Temperature: The rate of reaction increases with increase in temperature. For most of the reactions, the rate of reaction becomes almost double with 10o rise in temperature.
Presence of catalyst: A catalyst generally increases the speed of a reaction.
Answer the following question :
The role of a catalyst is to change _____.
A certain physiologically important first-order reaction has activation energy equal to at normal body temperature Without a catalyst, the rate constant for the reaction is . To be effective in the human body, where the reaction is catalysed by an enzyme, the rate constant must be at least If the activation energy is the only factor affected by the presence of the enzyme, by how much must the enzyme lower the activation energy of the reaction to achieve the desired rate? (Report your answer by multiplying with 10 and rounding off to two significant figures)
A certain physiologically important first-order reaction has activation energy equal to at a normal body temperature Without a catalyst, the rate constant for the reaction is . To be effective in the human body, where the reaction is catalysed by an enzyme, the rate constant must be at least . If the activation energy is the only factor affected by the presence of the enzyme, by how much must the enzyme lower the activation energy of the reaction to achieve the desired rate? Give answer to the nearest integer value after multiplying with 10.
After rise in temperature, the activation energy will:
What type of inhibitor is aspirin?
Penicillin acts as an inhibitor.
If in a unimolecular reaction, takes place according to the mechanism
I.
II.
where are the rate constants and P, and stand for product molecule, normal molecules of reactants and activated molecules of reactants respectively.
Which of the following statements are correct?
For next two question please follow the same
If in a unimolecular reaction, products takes place according to the mechanism
I.
II.
where are the rate constants and P, and stand for product molecule, normal molecules of reactants and activated molecules of reactants respectively.
Which of the following expressions are correct?
If a reaction is exothermic to the extent of and the forward reaction has an activation energy , the activation energy for the reverse reaction is
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction ______.
The role of a catalyst is to change _____.
Consider the reaction
The rate law for the reaction is rate =
In the presence of the reaction occurs in the following elementary steps:
Identify rate determining step.
Consider the reaction
The rate law for the reaction is rate = In the presence of the reaction occurs in the following elementary steps:
Identify (a) catalyst.
Comment on the effect of catalyst on rate of reverse reaction.
Comment on the effect of catalyst on rate of forward reaction.
The reaction between and occurs in the following steps:
The reaction intermediate in the reaction is
The rate constant for a reaction at is . What is the frequency factor of the reaction if its energy of activation is .
The rate law for the reaction is given by rate . The reaction occurs in the following steps:
Identify the slow step.
